스프링 부트와 AWS로 혼자 구현하는 웹 서비스
스프링 부트와 AWS로 웹 서비스를 구현한다. JPA와 JUnit 테스트, 그레이들, 머스테치, 스프링 시큐리티를 활용한 소셜 로그인 등으로 애플리케이션을 개발하고, 뒤이어 AWS 인프라의 기본 사용법과
www.aladin.co.kr
위의 책을 따라가면서 정리 + 궁금한 부분을 정리합니다.
1) Spring Security
https://winter1396love.tistory.com/28
Spring Security - SpringConfig
package com.lemint.book.springboot.config.auth; import com.lemint.book.springboot.domain.user.Role; import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor; import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.b..
winter1396love.tistory.com
2022-07-12
5장 스프링 시큐리티와 OAuth2.0으로 로그인 기능 구현하기을 진행하면서 막혔던 부분과 개념을 1차적으로 정리하고 있습니다.
따로 분리 할 예정
우선 스프링 시큐리티 1.5와 2.0의 연동 방법은 크게 변경 되었지만 설정 방법에서는 큰 차이가 없는 상황입니다.
위의 상황이 가능한 이유는
spring-security-oauth2-autoconfigure 라이브러리 덕분입니다.
해당 라이브러리는 2.0에서도 1.5의 설정을 그대로 사용 할 수 있게 해줍니다.
인터넷을 통해서 자료들을 볼때
spring-security-oauth2-autoconfigure 라이브러리와
application.properties, application.yml의 정보를 확인해본다.
우선 구글 서비스 등록을 해주어야한다.
구글 클라우드 플랫폼 주소 (https://console.cloud.google.com)으로 접속한다.


프로젝트 선택 -> 새 프로젝트 -> 만들기
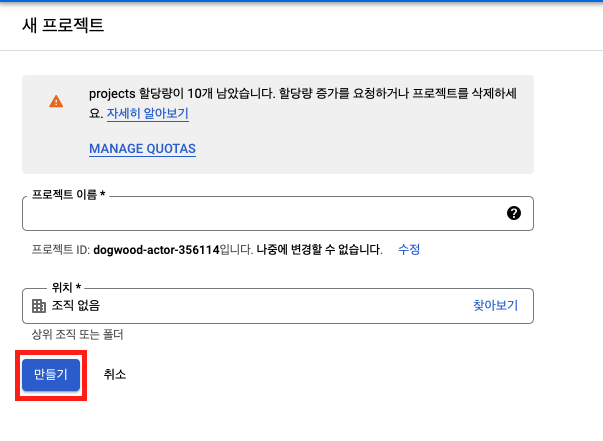
생성 후 API 및 서비스 -> 사용 설정된 API 및 서비스
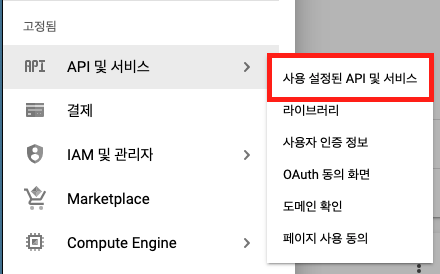
OAuth 동의 화면 -> 만들기
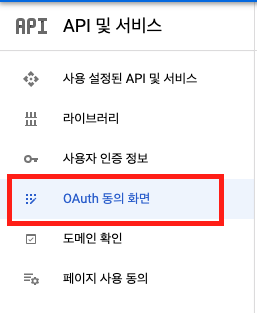
앱이름, 사용자 지원 이메일, 아래의 개발자 연락처 정보
계속 - 계속 - 계속 - 대시보드로 돌아가기
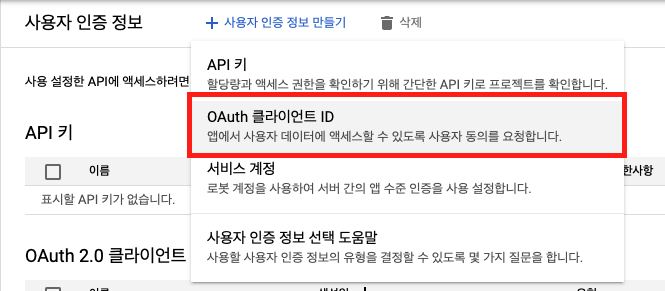
사용자 인증 정보 - 사용자 인증 정보 만들기
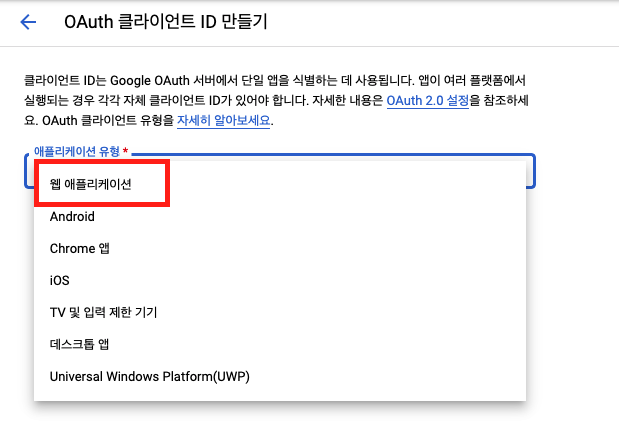
유형 - 웹 애플리케이션

생성 완료!
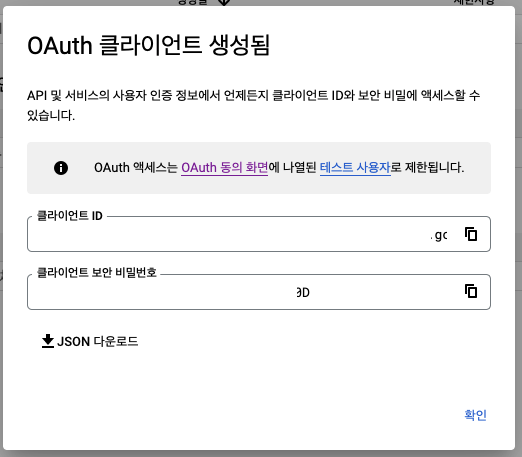
클라이언트 ID, 보안 비밀번호 -> properties 사용
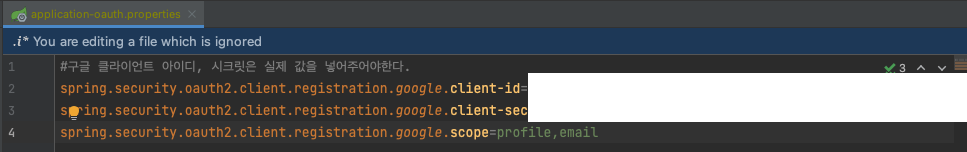
scope=profile,email
- 많은 예제에서는 이 scope를 별도로 등록하지 않고 있습니다.
- 기본값이 openid,profile,email이기 때문입니다.
- 강제로 profile,email를 등록한 이유는 openid라는 scope가 있으면 Open id Provider로 인식하기 때문입니다.
- 이렇게 되면 Open id Provider인 서비스(구글)와 그렇지 않은 서비스(네이버/카카오 등)로 나눠서 각각 OAuth2Service를 만들어야 합니다.
- 하나의 OAuth2Service로 사용하기 위해 일부러 openid scope를 빼고 등록합니다.
open id provider
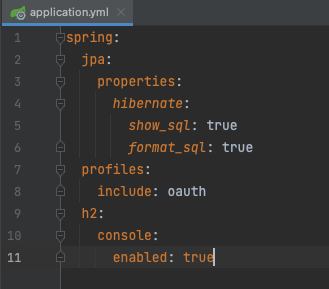
application.yml
spring: profiles: include: oauth 추가해준다
User 클래스 생성
package com.lemint.book.springboot.domain.user;
import com.lemint.book.springboot.domain.BaseTimeEntity;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import javax.persistence.*;
@Getter
@NoArgsConstructor
@Entity
public class User extends BaseTimeEntity {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
@Column(nullable = false)
private String name;
@Column(nullable = true)
private String email;
@Column
private String picture;
@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
@Column(nullable = false)
private Role role;
@Builder
public User(String name, String email, String picture, Role role) {
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.picture = picture;
this.role = role;
}
public User update(String name, String picture) {
this.name = name;
this.picture = picture;
return this;
}
public String getRoleKey(){
return this.role.getKey();
}
}- @Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
- JPA로 데이터베이스로 저장할 때 Enum 값을 어떤 형태로 저장할지를 결정합니다.
- 기본적으로 int로 숫자가 저장됩니다.
- 숫자로 저장되면 데이터베이스로 확인할 때 그 값이 무슨 코드를 의미하는지 알 수가 없습니다.
- 그래서 문자열(EnumType.STRING)로 지정될 수 있도록 선언합니다.
각 사용자의 권한을 관리할 Enum 클래스 Role을 생성합니다.
ROLE
package com.lemint.book.springboot.domain.user;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
@Getter
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public enum Role {
/**
* 스프링 시큐리티에서는 권한 코드 앞에 항상 ROLE_ 이 앞에 존재해야한다.
* */
GUEST("ROLE_GUEST", "손님"),
USER("ROLE_USER", "일반 사용자");
private final String key;
private final String title;
}
UserRepository
package com.lemint.book.springboot.domain.user;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import java.util.Optional;
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
Optional<User> findByEmail(String Email);
}findByEmail
- 소셜 로그인으로 반환되는 값 중 email을 통해 이미 생성된 사용자인지 처음 가입하는 사용자인지 판단하기 위한 메소드입니다.
build.gradle
implementation('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client')spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client
- 소셜 로그인 등 클라이언트 입장에서 소셜 기능 구현 시 필요한 의존성
- spring-boot-starter-oauth2-client와 spring-security-oauth2-jose를 기본으로 관리해줍니다.
SecurityConfig (config > auth)
package com.lemint.book.springboot.config.auth;
import com.lemint.book.springboot.domain.user.Role;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@EnableWebSecurity //Spring Security 설정들을 활성화시켜 준다.
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
private final CustomOAuth2UserService customOAuth2UserService;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
/**
* csrf().disable().headers().frameOptions().disable() :
* h2-console 화면 사용을 위해 해당 옵션들을 disable
* */
.csrf().disable()
.headers().frameOptions().disable()
.and()
/**
* authorizeRequests() :
* URL별 권한 관리를 설정하는 옵션의 시작점, authorizeRequests가 선언 되어야만 antMachers옵션을 사용 할 수 있다
* */
.authorizeRequests()
/**
* antMatchers() :
* 권한 관리 대상을 지정하는 옵션, URL과 HTTP 메소드별로 관리가 가능하다.
* "/" 등 지정된 URL들은 permitAll() 옵션으로 전체 권한을 줌
* "/api/v1/**" 주소를 가진 API는 USER 권한을 가진 사람만 가능하게
* */
.antMatchers("/", "/css/**", "/images/**", "/js/**", "/h2-console/**", "/profile").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/api/v1/**").hasRole(Role.USER.name())
/**
* anyRequest() :
* 설정된 값들 이외 나머지 URL들을 나타낸다.
*
* authenticated() :
* 추가하여 나머지 URL들은 모두 인증된 사용자(로그인한 사용자)들에게만 허용한다.
* */
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
/**
* logout().logoutSuccessUrl("/") :
* 로그아웃 기능에 대해서 여러 설정의 진입점
* 로그아웃 성공시 "/" 주소로 이동
* */
.logout()
.logoutSuccessUrl("/")
.and()
/**
* oauth2Login() :
* OAuth2 로그인 기능에 대한 설정의 진입점.
* */
.oauth2Login()
/**
* userInfoEndpoint() :
* OAuth2 로그인 성공 이후 사용자 정보를 가져올 설정 담당
* */
.userInfoEndpoint()
/**
* userService
* 소셜 로그인 성공 시 후속 조치를 진행할 UserService 인터페이스의 구현체를 등록한다.
* 리소스 서버에서 사용자 정보를 가져온 상태에서 추가로 진행하고자 하는 기능을 명시 할 수 있다.
* */
.userService(customOAuth2UserService);
}
}
CustomOAuth2UserService
package com.lemint.book.springboot.config.auth;
import com.lemint.book.springboot.config.auth.dto.OAuthAttributes;
import com.lemint.book.springboot.config.auth.dto.SessionUser;
import com.lemint.book.springboot.domain.user.User;
import com.lemint.book.springboot.domain.user.UserRepository;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.security.core.authority.SimpleGrantedAuthority;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.userinfo.DefaultOAuth2UserService;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.userinfo.OAuth2UserRequest;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.client.userinfo.OAuth2UserService;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.user.DefaultOAuth2User;
import org.springframework.security.oauth2.core.user.OAuth2User;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.util.Collections;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Service
public class CustomOAuth2UserService implements OAuth2UserService<OAuth2UserRequest, OAuth2User>{
private final UserRepository userRepository;
private final HttpSession httpSession;
@Override
public OAuth2User loadUser(OAuth2UserRequest userRequest) {
OAuth2UserService<OAuth2UserRequest, OAuth2User> delegate = new DefaultOAuth2UserService();
OAuth2User oAuth2User = delegate.loadUser(userRequest);
/**
* registrationId :
* 현재 로그인 진행중인 서비스를 구분하는 코드
* */
String registrationId = userRequest.getClientRegistration().getRegistrationId();
/**
* userNameAttributeName :
* OAuth2 로그인 진행 시 키가 되는 필드값. Primary Key 같은 존재
* */
String userNameAttributeName = userRequest.getClientRegistration().getProviderDetails()
.getUserInfoEndpoint().getUserNameAttributeName();
/**
* OAuthAttributes :
* OAuth2UserService를 통해서 가져온 OAuth2User 의 attribute를 담을 클래스
* */
OAuthAttributes attributes = OAuthAttributes.of(registrationId, userNameAttributeName, oAuth2User.getAttributes());
User user = saveOrUpdate(attributes);
/**
* SessionUser :
* 세션에 사용자 정보를 저장하기 위한 Dto 클래스
* */
httpSession.setAttribute("user", new SessionUser(user));
return new DefaultOAuth2User(Collections.singleton(new SimpleGrantedAuthority(user.getRoleKey())),
attributes.getAttributes(),
attributes.getNameAttributeKey());
}
private User saveOrUpdate(OAuthAttributes attributes) {
User user = userRepository.findByEmail(attributes.getEmail())
.map(entity -> entity.update(attributes.getName(), attributes.getPicture()))
.orElse(attributes.toEntity());
return userRepository.save(user);
}
}
OAuthAttributes (config > auth > dto)
package com.lemint.book.springboot.config.auth.dto;
import com.lemint.book.springboot.domain.user.Role;
import com.lemint.book.springboot.domain.user.User;
import lombok.Builder;
import lombok.Getter;
import java.util.Map;
@Getter
public class OAuthAttributes {
private Map<String, Object> attributes;
private String nameAttributeKey;
private String name;
private String email;
private String picture;
@Builder
public OAuthAttributes(Map<String, Object> attributes, String nameAttributeKey, String name, String email, String picture) {
this.attributes = attributes;
this.nameAttributeKey = nameAttributeKey;
this.name = name;
this.email = email;
this.picture = picture;
}
public static OAuthAttributes of(String registrationId, String userNameAttributeName,
Map<String, Object> attributes){
return ofGoogle(userNameAttributeName, attributes);
}
private static OAuthAttributes ofGoogle(String userNameAttributeName, Map<String, Object> attributes) {
return OAuthAttributes.builder()
.name((String) attributes.get("name"))
.email((String) attributes.get("email"))
.picture((String) attributes.get("picture"))
.attributes(attributes)
.nameAttributeKey(userNameAttributeName)
.build();
}
public User toEntity() {
return User.builder()
.name(name)
.email(email)
.picture(picture)
.role(Role.GUEST)
.build();
}
}- of()
- OAuth2User에서 반환하는 사용자 정보는 Map이기 때문에 값 하나하나를 변환해야만 합니다.
- toEntity
- User 엔티티를 생성합니다.
- OAuthAttributes에서 엔티티를 생성하는 시점은 처음 가입할 때입니다.
- 가입할 때의 기본 권할을 GUEST로 주기 위해서 role 빌더값에는 Role.GUEST를 사용합니다.
- OAuthAttributes 클래스 생성이 끝났으면 같은 패키지에 SessionUser 클래스를 생성합니다.
SessionUser (config > auth > dto)
package com.lemint.book.springboot.config.auth.dto;
import com.lemint.book.springboot.domain.user.User;
import lombok.Getter;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Getter
public class SessionUser implements Serializable {
private String name;
private String email;
private String picture;
public SessionUser(User user) {
this.name = user.getName();
this.email = user.getEmail();
this.picture = user.getPicture();
}
}
SessionUser에는 인증된 사용자 정보만 필요합니다.
@Entity User 클래스를 SessionUser로 사용안하는 이유
세션에 저장하기 위해 User클래스를 세션에 저장하려고 하니 User 클래스에 직렬화를 구현하지 않았다는
에러가 난다.
- Entity 클래스는 직렬화 코드를 넣지 않는게 좋다
- 엔티티 클래스에는 언제 다른 엔티티와 관계가 형성될지 모른다.
- @OneToMany, @ManyToMany등 자식 엔티티를 갖고 있다면 직렬화 대상에 자식들까지 포함되니 성능 이슈, 부수 효과가 발생할 확률이 높다
그래서 직렬화 기능을 가진 세션 Dto를 하나 추가로 만든 것이 더 좋은 방법이다.
index는 생략한다.
IndexController
package com.lemint.book.springboot.web;
import com.lemint.book.springboot.config.auth.dto.SessionUser;
import com.lemint.book.springboot.service.posts.PostsService;
import com.lemint.book.springboot.web.dto.PostsResponseDto;
import lombok.RequiredArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerTypePredicate;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Controller
public class IndexController {
private final PostsService postsService;
private final HttpSession httpSession;
@GetMapping("/")
public String index(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("posts", postsService.findAllDesc());
/**
* 앞서 작성된 CustomerOAuthUserService에서 로그인 성공 시 세션에서 SessionUser를 저장하게 구현
* 로그인을 성공하면 httpSession.getAttribute("user") 을가져와서 SessionUser에 담는다.
* */
SessionUser user = (SessionUser) httpSession.getAttribute("user");
if(user != null) {
model.addAttribute("userName", user.getName());
}
return "index";
}
@GetMapping("/posts/save")
public String postsSave() {
return "posts-save";
}
@GetMapping("/posts/update/{id}")
public String postsUpdate(@PathVariable Long id, Model model){
PostsResponseDto dto = postsService.findById(id);
model.addAttribute("post", dto);
return "posts-update";
}
}- (SessionUser) httpSession.getAttribute("user")
- 앞서 작선된 CustomOAuth2UserService에서 로그인 성공 시 세션에 SessionUser를 저장하도록 구성했습니다.
- 즉, 로그인 성공시 httpSerssion.getAttribute("user")에서 값을 가져올 수 있습니다.
- if(user != null)
- 세션에 저장된 값이 있을 때만 model에 userName으로 등록
실행 화면

Google Login
로그인 정보가 표시 된다.
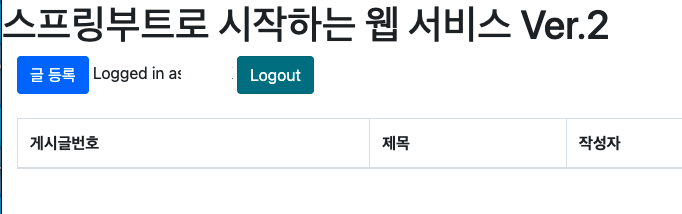
로그인 성공~
혹시 모르니 H2Console을 접속해보자

로그인 성공이지만 오르쪽 끝 ROLE을 보면 GUEST인 상태이다 GUEST는 게시글 등록이 불가능 하다.
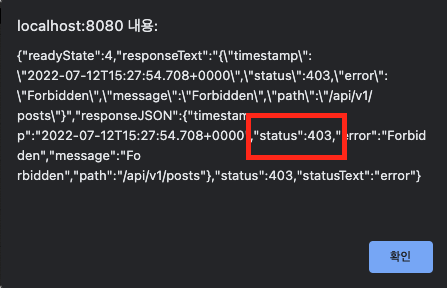
사용자 권한을 수정해주자
update user set role = 'USER';
권한 수정 후 재등록
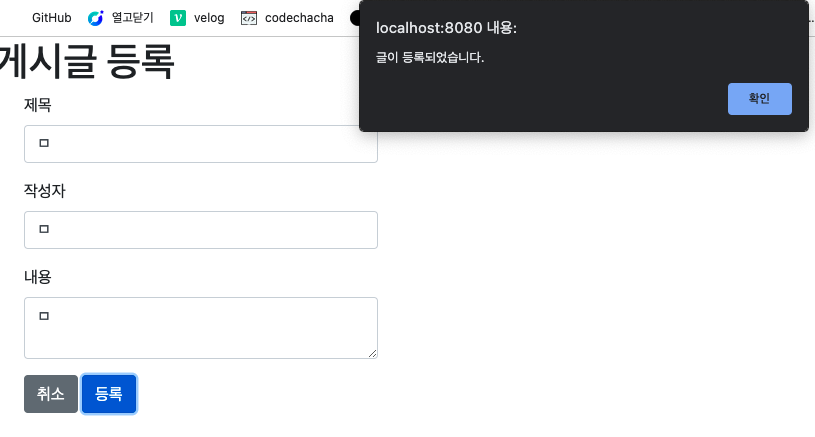
무사히 등록 된다!
'개인적 정리' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring Security - SpringConfig (0) | 2022.07.10 |
|---|---|
| Spring - security 사용시 properties, gradle (0) | 2022.07.10 |
| @Respository 어노테이션이 필수가 아니다? (0) | 2022.06.12 |
| 알고리즘 PULL 까먹지 말아보자 (0) | 2022.06.06 |
| 테스트 코드 (1) | 2022.04.17 |
